Introduction¶
One of the key DBSnapper features is the ability to easily share sanitized database snapshots with your team, developers, testers, and other stakeholders. Sharing snapshots is useful for providing sanitized data for development, testing, and other purposes without exposing sensitive information.
By utilizing your own private cloud storage providers, you can securely store your snapshots in your own approved infrastructure and use the DBSnapper Agent and Cloud to facilitate easy sharing.
Sharing Architecture¶
The DBSnapper sharing architecture is designed to allow you to create snapshots of your database and share the unsanitized and sanitized snapshots in separate locations. You can then share the sanitized cloud storage location with your team and they can use the DBSnapper agent to access and load these snapshots.
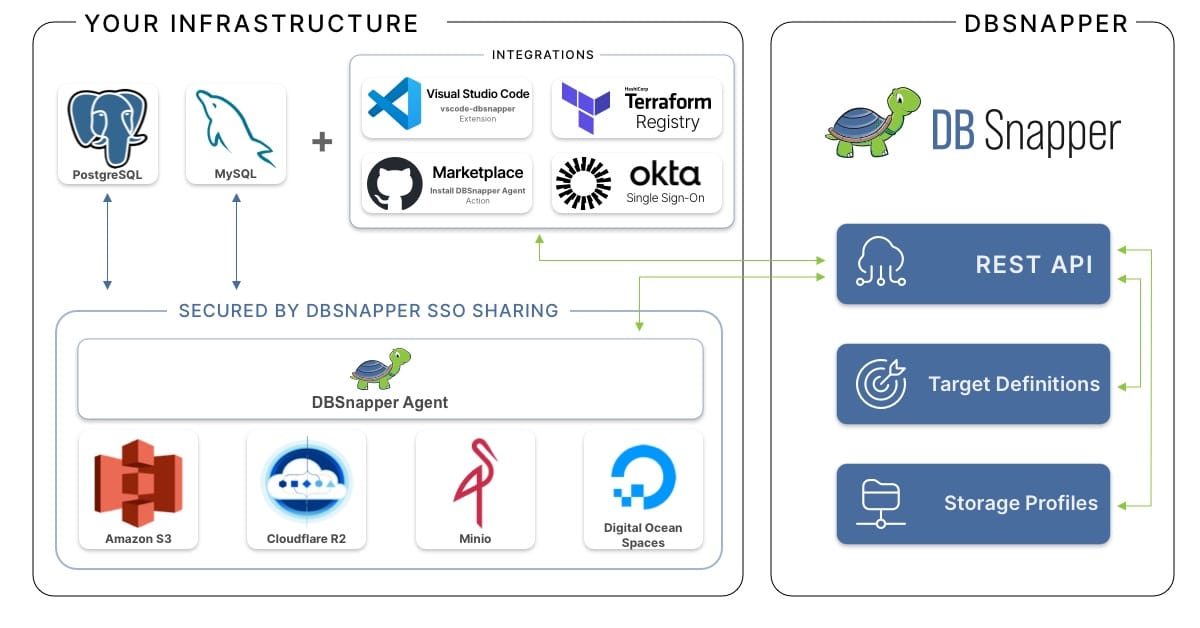
DBSnapper Architecture Overview
Getting Started¶
To get started with using a cloud storage engine, you will need to configure a storage_profile in your DBSnapper configuration file. The storage_profile configuration specifies the cloud storage provider, credentials, and bucket information for the storage engine.
AWS S3 configuration examples
In the example above we have two storage_profiles configurations for AWS S3. The first configuration s3-with-provided-credentials explicitly specifies the access key, secret key, region, and bucket for an S3 storage engine. s3-from-awscli-shared-profile, on the other hand, indicates that we want to retrieve the credentials from the dbsnapper_credentials AWS shared configuration profile as specified in the awscli_profile field.
We have also defined a share target configuration on line 19 that uses the s3-from-awscli-shared-profile storage profile to access shared snapshots from the dbsnapper-test-s3 bucket. These shared snapshots will be loaded into the dbsnapper_test database as specified in the dst_url field on line 23.