Release Notes
Full release notes
For a complete list of changes, see the DBSnapper Releases Page which will include all changes, bug fixes, and enhancements.
v2.7.0 - Team Sharing for SSO Groups¶
This release introduces the ability to share targets and snapshots with your team members via their assigned groups in their SSO provider (currently Okta). You can specify the groups on the Targets page and the agent will include these targets and snapshots for any members of the group.
Other Changes:
- Using presigned URLs for snapshot uploads and downloads from cloud storage.
- Added flags
--originaland--destdbto thetargetsandtargetcommands so these can be used whenpulling orloading snapshots in the terminal UI. - Specify a default destination database (used for loading shared targets) in the configuration file like so:
defaults:
shared_target_dst_db_url: postgres://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/dbsnapper_dst_db_default
v2.6.0 - Overrides: Sanitization Query¶
You may now specify a sanitization query that can be used to override all sanitization operations. This can be provided in the configuration file or as an environment variable and must be base-64 encoded:
override:
san_query: RFJPUCBUQUJMRSBJRiBFWElTVFMgZGJzbmFwcGVyX2luZm87CkNSRUFURSBUQUJMRSBkYnNuYXBwZXJfaW5mbyAoY3JlYXRlZF9hdCB0aW1lc3RhbXAsIHRhZ3MgdGV4dCBbXSk7CklOU0VSVCBJTlRPIGRic25hcHBlcl9pbmZvIChjcmVhdGVkX2F0LCB0YWdzKQpWQUxVRVMgKE5PVygpLCAne3F1ZXJ5OnNhbl9xdWVyeV9vdmVycmlkZSwgbG9jYXRpb246Y2xvdWR9Jyk7
Or via an environment variable:
DBSNAPPER_OVERRIDE__SAN_QUERY=RFJPUCBUQUJMRSBJRiBFWElTVFMgZGJzbmFwcGVyX2luZm87CkNSRUFURSBUQUJMRSBkYnNuYXBwZXJfaW5mbyAoY3JlYXRlZF9hdCB0aW1lc3RhbXAsIHRhZ3MgdGV4dCBbXSk7CklOU0VSVCBJTlRPIGRic25hcHBlcl9pbmZvIChjcmVhdGVkX2F0LCB0YWdzKQpWQUxVRVMgKE5PVygpLCAne3F1ZXJ5OnNhbl9xdWVyeV9vdmVycmlkZV9FTlYsIGxvY2F0aW9uOmNsb3VkfScpOw== dbsnapper sanitize dvdrental-san -n
Note: Remember to base-64 encode the query before providing it in the configuration file or as an environment variable.
v2.5.3 - Detect Terminal (TTY)¶
- TTY detection has been added to the
targetsandtargetcommands. If a TTY is detected, the interactive Terminal UI will load, otherwise a non-interactive ascii table will be displayed.
v2.5.2 - Bugfixes¶
- Fix parsing snapshot filename with multiple underscores.
v2.5.1 - Decrypt Authtoken When Provided via Environment + bugfixes¶
- Will now attempt to decrypt the authtoken if an encrypted authtoken is provided via the DBSNAPPER_AUTHTOKEN environment variable.
v2.5.0 - Docker in Docker Changes + Environment Variables + Destination DB Override Flag¶
This release fixes some issues when running DBSnapper agent in a Docker-in-Docker (DinD) environment and adds some additional nice features.
Docker in Docker Ephemeral Sanitization Changes¶
This was caused by limitations in the way Docker manages DinD containers and directory mounts. In summary - when creating a container to do dumps and restores in a DinD environment, the mountpoint was relative to the Host and not the DinD container. This caused the container to not be able to access the mounted directory. We now use the local database tools which are installed in the dbsnapper agent container to do the dumps and restores, avoiding this issue.
The ephemeral container is still started as normal in a DinD environment and will be placed in the dbsnapper network. Using a non-default Docker network is necessary to ensure the Docker internal DNS resolver is used to resolve container hostnames correctly.
Notes - Ephemeral sanitization in DinD environments:¶
- DBSnapper, by default, specifies
dbsnapperfor the docker network for any containers created. - If you are running the DBSnapper docker image and planning to do an ephemeral sanitization, you'll need to
- Mount the docker socket to the container
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock - Specify the
dbsnappernetwork for the container--network dbsnapper
Environment Variables¶
This release also improves handling of environment variables. You can now execute the docker container without the need to initialize the configuration file first. You can pass the environment variables directly to the docker run command. For example:
Interactive Agent Example¶
docker run -it -e DBSNAPPER_SECRET=XXX -e DBSNAPPER_AUTHTOKEN=YYY -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --rm --network dbsnapper --pull always ghcr.io/dbsnapper/dbsnapper:latest /bin/bash
This will start the DBSnapper agent container in interactive mode with the following settings:
- With the
DBSNAPPER_SECRETandDB_SNAPPER_AUTHTOKENenvironment variables set. Both are required to execute the agent without a configuration file. - With the docker socket mounted to the container
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock(for ephemeral sanitization) - In the
dbsnappernetwork--network dbsnapper - Will pull the latest DBSnapper image
--pull always - Will remove the container after it exits
--rm
One-Liner Snapshot Example¶
A one-liner that will launch the DBSnapper agent container, build a snapshot, upload it to the cloud, and exit:
docker run -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -e DBSNAPPER_SECRET_KEY=XXX -e DBSNAPPER_AUTHTOKEN=YYY --rm --network dbsnapper --pull always ghcr.io/dbsnapper/dbsnapper:latest dbsnapper build dvdrental-cloud
This command will output:
Creating working directory at: /root/.dbsnapper
DBSnapper Agent - Version: 2.5.0
DBSnapper Cloud: Enabled
START: Build Snapshot for target: dvdrental-cloud with engine: postgres-local
--> Zipping snapshot to /root/.dbsnapper/1715957602_dvdrental-cloud.zip
--> Uploading snapshot to Cloud Storage Profile: cloudflare-r2 - r2://dbsnapper-r2/dbs-production-bucket/e9b33f60-d791-4d73-b9d2-30f9adad2fde.zip
--> Upload complete.
--> Local snapshot entry stored in cloud, ID: e9b33f60-d791-4d73-b9d2-30f9adad2fde
FINISH: Building DB Snapshot for target: dvdrental-cloud
One-Liner Sanitize Example¶
A one-liner that will launch the DBSnapper agent container, create a new original and sanitized snapshot set, upload them to cloud storage, and exit:
docker run -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -e DBSNAPPER_SECRET_KEY=XXX -e DBSNAPPER_AUTHTOKEN=YYY --rm --network dbsnapper --pull always ghcr.io/dbsnapper/dbsnapper:latest dbsnapper sanitize dvdrental-cloud -n
Which outputs:
latest: Pulling from dbsnapper/dbsnapper
Digest: sha256:2d0b3c054942bdea88bde16e8b49a69d1249a0ea20b78b69508b23e4ee23f92d
Status: Image is up to date for ghcr.io/dbsnapper/dbsnapper:latest
Creating working directory at: /root/.dbsnapper
DBSnapper Agent - Version: 2.5.0 (c2d2ec052fe4) Build Date: 2024-05-17T16:21:43Z
DBSnapper Cloud: Enabled
Running ephemeral sanitization
Creating a new snapshot set
--> Building NEW original snapshot
--> Zipping snapshot to /root/.dbsnapper/1715963288_dvdrental-san.zip
--> Created ephemeral container: animal-belief, database: pgdocker://dbsnapper:dbsnapper@nutrition/troupe
--> Restoring snapshot to Sanitization DB
--> Sanitizing Snapshot
--> Building sanitized snapshot
--> Pushing original snapshot to cloud
--> Uploading snapshot to Cloud Storage Profile: R2-Original - r2://dbsnapper/original/0bd58a2a-4db1-49a8-8917-f513d829c31b.zip
--> Upload complete.
--> Local snapshot entry stored in cloud, ID: 0bd58a2a-4db1-49a8-8917-f513d829c31b
--> Pushing sanitized snapshot to cloud
--> Uploading snapshot to Cloud Storage Profile: R2-Sanitized - r2://dbsnapper/sanitized/cb062d1f-cf2d-4bae-a1b0-489853e5a500.san.zip
--> Upload complete.
--> Local snapshot entry stored in cloud, ID: cb062d1f-cf2d-4bae-a1b0-489853e5a500
Sanitize Complete
Environment Variables for Non-Docker Environments¶
Of course, you can always use envirnoment variables when running the DBSnapper agent in a non-Docker environment as well.
This will list all targets using the specified secret key and authtoken. If you don't have a configuration file, it will end up listing all targets created in the DBSnapper cloud.
Destination Database Override Flag¶
The load command now supports a --destdb flag that can be used to override the snapshot destination database specified in the target configuration. The following example overrides the database set for the target-name target with the postgres://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/database_snapshot_override database:
dbsnapper load target-name --destdb="postgres://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/database_snapshot_override"
v2.4.0 - Ephemeral Sanitization Support¶
This release is bringing back the ability to use ephemeral containers for sanitization. This streamlines the sanitization process, leveraging containers to spin up a temporary database that can be used to sanitize the unsanitized snapshot data.
The sanitize command now behaves as follows:
- It will create a new unsanitized and sanitized snapshot set if no snapshots exist for a target or the
-nflag is set. - Will use an ephemeral container to sanitize the data if the
sanitize: dst_urlis not specified in the configuration file, or the-eflag is set.
You can combine both the -n and -e flags to create a new snapshot set and use an ephemeral container for sanitization.
v2.3.0 - New User Interface, Share Targets, Storage Engines Improvements, and More¶
A Terminal User Interface (TUI) has been added to the DBSnapper Agent, making it even easier to use. See all your targets, drill down into their snapshots, and load them all from the new UI.
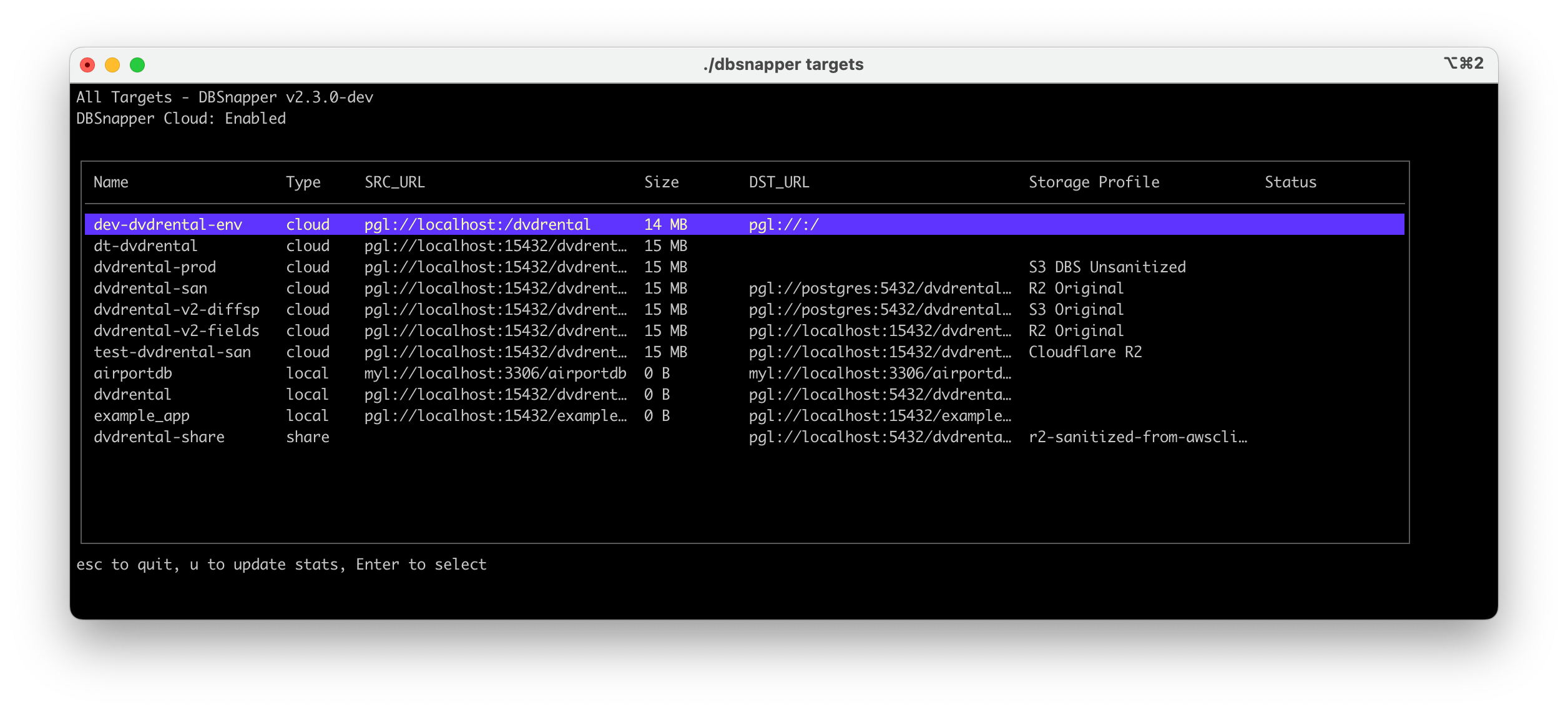
DBSnapper Agent User Interface - All Targets
Sharing Targets have been added to DBSnapper. Leveraging the ability to specify different storage profiles for original and sanitized snapshots, you can now create a share target in your configuration file, that will allow you to list and load sanitized snapshots from a shared storage location. This is useful for sharing sanitized snapshots with developers, testers, and other stakeholders.
New Storage Engines have been added. In addition to our support for AWS S3 and CloudFlare R2, we have added support for Minio and Digital Ocean Spaces
Storage Engines now support retrieving credentials from the AWS CLI shared configuration. It is now possible to retrieve S3 compatible storage engine credentials from environment variables, or you can specify an awscli_profile in your storage profile configuration to use the credentials from the specified AWS CLI profile. More information on this can be found in the Storage Engine Configuration documentation.
v2.2.0 - Separate Storage Profiles for Unsanitized and Sanitized Snapshots¶
You can now specify different storage profiles for unsanitized (original) and sanitized snapshots, allowing you to store them in different buckets or cloud providers if desired. This will allow sharing only the sanitized snapshot cloud storage buckets with developers, while keeping the unsanitized snapshots private.
Up next is additional sharing functionality for accessing and loading the sanitized snapshots.
Download the v2.2.0 release for your platform.
v2.1.0 - Connection String URL Templates¶
All connection string URLs now support templating. This allows you to access environment variables in the connection string URLs. For example, you can now use the following connection string URL for a Postgres database:
snapshot:
src_url: postgres://{{`DB_USER` | env}}:{{`DB_PASSWORD` | env}}@localhost:5432/{{`DB_NAME` | env}}
In this example we are indicating we want the username, password, and database name to be read from the DB_USER, DB_PASSWORD, and DB_NAME environment variables, respectively.
Templates conform to Go Templates syntax. Specify the env function to read the value from the environment.
{{`ENV_VAR` | env}} # substitute the value of the ENV_VAR environment variable
{{`CONSTANT`}} # substitute the supplied `CONSTANT` value
v2.0.0 - Subsetting!¶
We're excited to announce the release of DBSnapper v2.0, which introduces a major new feature: Database Subsetting. This feature allows you to create a relationally consitent copy of your database that contains only a subset of the data. This is useful for creating smaller, more manageable datasets for development and testing.
Backwards Compatibility
This release introduces a new configuration file format and options. If you are upgrading from a previous version, you will need to update your configuration file to the new format. See the Configuration Settings documentation for more information.
Additional Improvements¶
- Improved support for MySQL databases.
- Support for PostgreSQL COPY protocol for fast data copy operations.
- Simplified the sanitization command, eliminating the use of ephemeral database containers,
- Released Docker images for easier installation and use.
- An extensive refactoring and testing of the codebase to improve performance, quality, and maintainability.
- Improved documentation and examples.