Quick Start Guide
This guide will walk you through creating your first database snapshot with DBSnapper in just a few minutes. You'll learn how to set up the agent, configure a target database, and create a sanitized snapshot for development use.
What You'll Accomplish¶
By the end of this guide, you will have:
- ✅ Configured the DBSnapper Agent
- ✅ Connected to a database (source)
- ✅ Created your first database snapshot
- ✅ Loaded the snapshot into a development database
Prerequisites¶
Before starting, ensure you have:
- DBSnapper Agent installed - See the installation guide for setup instructions
- A source database - PostgreSQL or MySQL database with sample data
- A destination database - Where you'll load the snapshot (can be empty)
- Database tools - Either installed locally or Docker available for containerized tools
Need a Test Database?
If you don't have a database ready, consider using the PostgreSQL dvdrental sample database or MySQL sakila database for testing.
Option 1: Container-Based Quick Start¶
The fastest way to get started is using the DBSnapper container with DBSnapper Cloud:
docker run -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
-e DBSNAPPER_SECRET_KEY=your_secret_key \
-e DBSNAPPER_AUTHTOKEN=your_auth_token \
--rm --network dbsnapper --pull always \
ghcr.io/dbsnapper/dbsnapper:latest \
dbsnapper build your-cloud-target
This approach requires:
- A DBSnapper Cloud account with configured targets
- Your secret key and auth token from the cloud dashboard
Option 2: Local Configuration Setup¶
For local development or when you want full control over configuration:
Step 1: Initialize Configuration¶
Initialize the configuration file¶
Run the config init command to create an example configuration at ~/.config/dbsnapper/dbsnapper.yml
Configuration file initialized to default values
Check the configuration and environment¶
Next, we can check our configuration and required dependencies. This runs some checks to verify the configuration file is valid and reports on the database tools found in the path as well as Docker engine and database image availability.
dbsnapper config check output
Checking DBSnapper Configuration
✅ Config file ( /Users/snappy/app/dbsnapper/cli/dbsnapper.yml ) found and loaded
🔵 Postgres Local Engine (pglocal)
✅ psql found at /Applications/Postgres.app/Contents/Versions/latest/bin/psql
✅ pg_dump found at /Applications/Postgres.app/Contents/Versions/latest/bin/pg_dump
✅ pg_restore found at /Applications/Postgres.app/Contents/Versions/latest/bin/pg_restore
🔵 MySQL Local Engine (mylocal)
✅ mysqldump found at /opt/homebrew/bin/mysqldump
✅ mysql found at /opt/homebrew/bin/mysql
🔵 Postgres Docker Engine (pgdocker)
✅ Docker client connected
✅ docker.images set in config file
✅ docker.images.postgres set in config file
✅ Found Docker image: postgres:latest
🔵 Mysql Docker Engine (mydocker)
✅ Docker client connected
✅ docker.images set in config file
✅ docker.images.mysql set in config file
✅ Found Docker image: mysql:8.0-oracle
✅ All supported database engines configured
✅ DBSnapper Cloud connected
✅ Configuration OK
Step 3: Configure Database Targets¶
Add database connection details to your configuration. A "target" defines both source and destination databases.
Open your configuration file (~/.config/dbsnapper/dbsnapper.yml) and add a target definition:
targets:
my_app:
snapshot:
src_url: postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/production_app?sslmode=disable
dst_url: postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/dev_app?sslmode=disable
Database Safety
The destination database (dst_url) will be completely dropped and recreated when loading a snapshot. Never use a production database as a destination.
Connection Examples
- PostgreSQL:
postgresql://user:password@host:port/database?sslmode=disable - MySQL:
mysql://user:password@host:port/database
Step 4: Verify Target Configuration¶
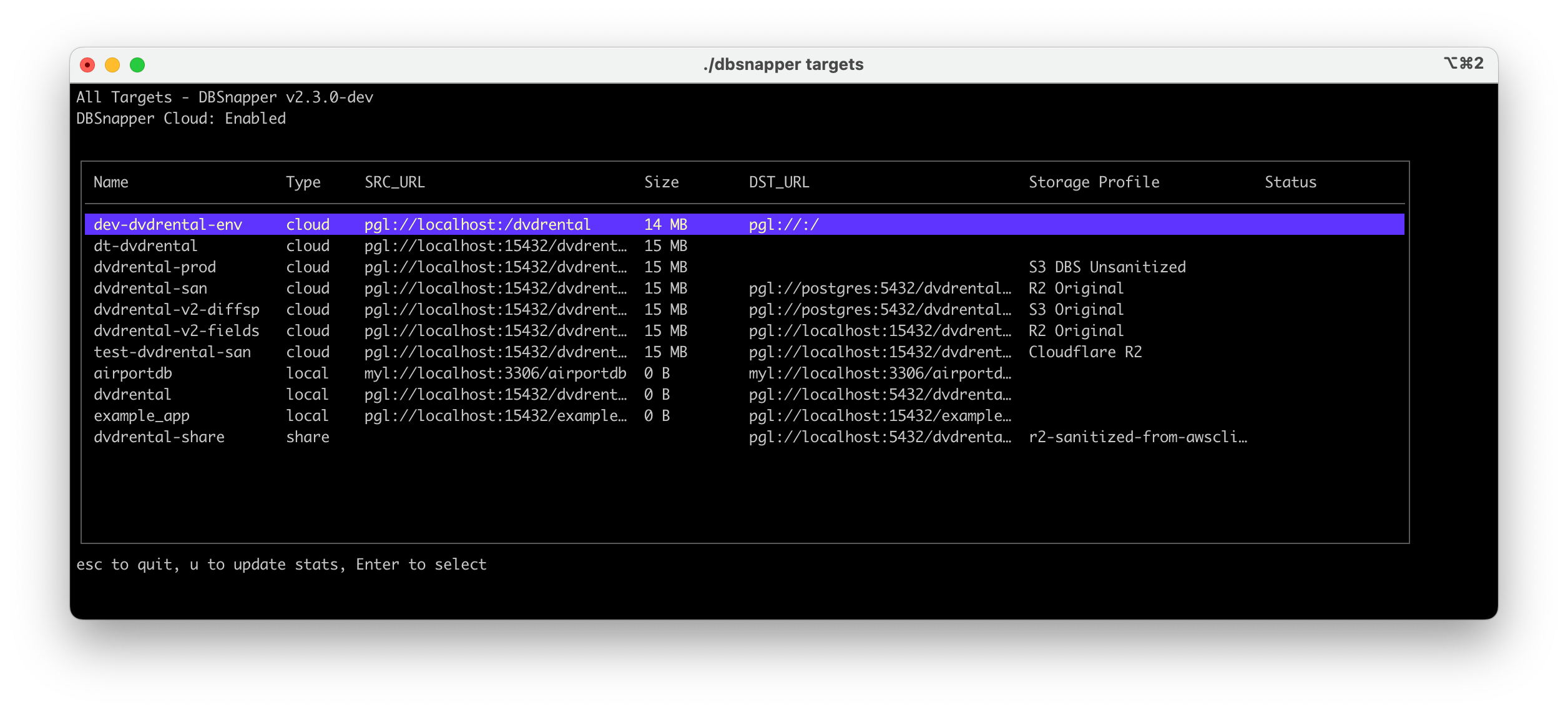
List all configured targets and verify connectivity:
This command displays all targets with their connection status and database sizes. The DBSnapper UI provides a clear overview:
Step 5: Create Your First Snapshot¶
Build a snapshot of your source database:
This command:
- Connects to your source database using the configured
src_url - Creates a database dump using native tools (
pg_dumpfor PostgreSQL,mysqldumpfor MySQL) - Stores the snapshot in your working directory
- Optionally uploads to cloud storage if configured
Snapshot Naming
Snapshots are automatically timestamped and indexed. You can also add custom tags or descriptions.
Step 6: View Available Snapshots¶
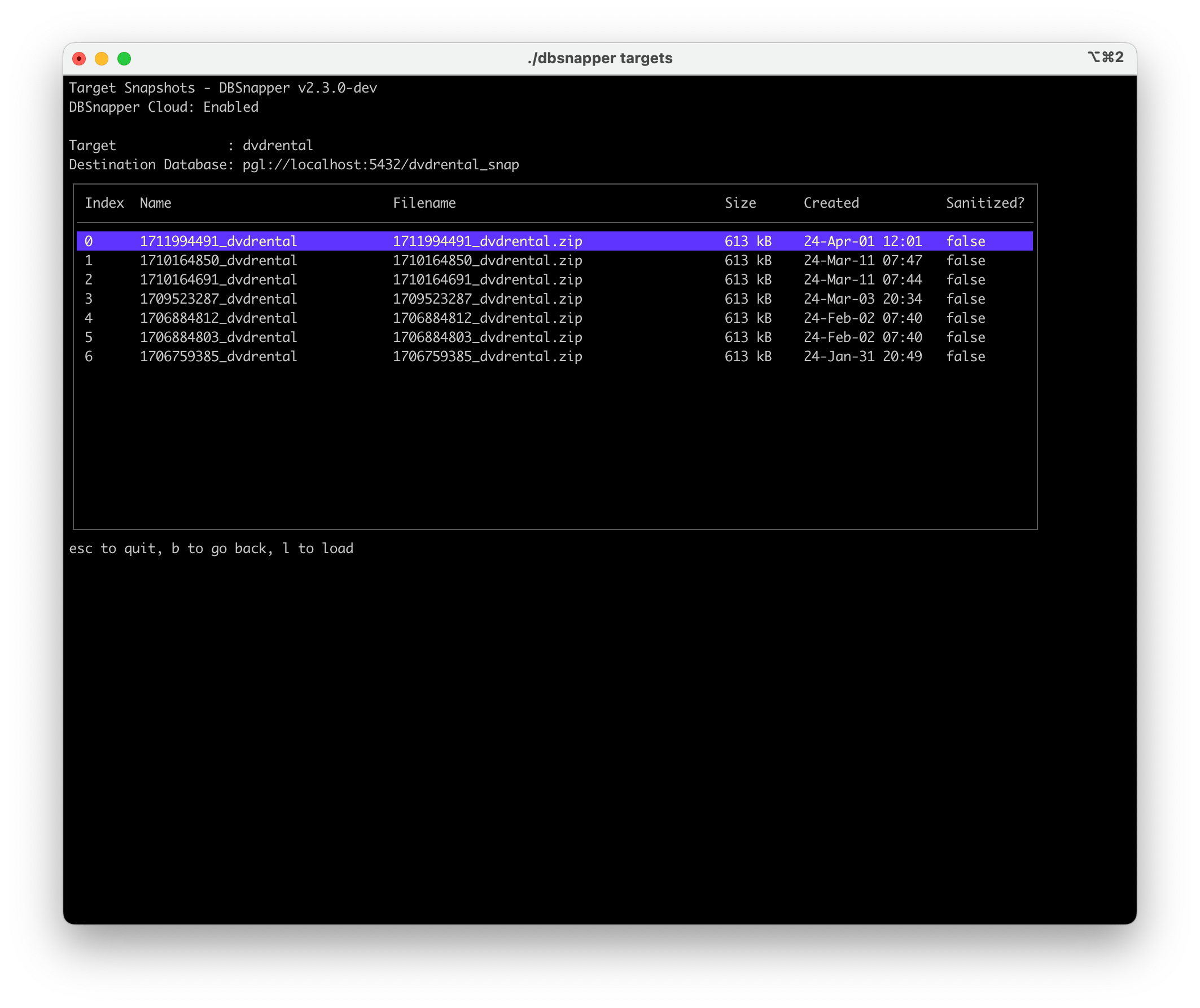
List all snapshots for a specific target:
This shows detailed information about each snapshot including size, creation time, and status:
Step 7: Load a Snapshot¶
Load the most recent snapshot (index 0) into your destination database:
Destructive Operation
The destination database will be completely dropped and recreated. Ensure you're not targeting a production database.
Congratulations! 🎉¶
You've successfully created and loaded your first database snapshot with DBSnapper. Your development database now contains a sanitized copy of your production data.
Next Steps¶
Now that you have the basics working, explore these advanced features:
Data Sanitization¶
Learn how to remove sensitive information from your snapshots:
- Sanitization Overview - Understanding data sanitization concepts
- Configure Sanitization Rules - Set up automated PII removal
Data Subsetting¶
Reduce snapshot size by including only relevant data:
- Subset Configuration - Create smaller, focused snapshots
Team Collaboration¶
Share snapshots securely with your team:
- DBSnapper Cloud - Central snapshot management
- Storage Profiles - Configure cloud storage
Automation & Integration¶
Integrate DBSnapper into your workflows:
- GitHub Actions - Automated CI/CD snapshots
- VS Code Extension - In-editor snapshot management
- Terraform Provider - Infrastructure as Code
Common Issues & Troubleshooting¶
Connection Problems: If dbsnapper targets shows connection errors, verify:
- Database credentials and network connectivity
- Database server is running and accepting connections
- SSL/TLS settings match your database configuration
Missing Tools: If dbsnapper config check reports missing tools:
- Install database tools locally (
postgresql-client,mysql-client) - Or use Docker-based engines (recommended for consistency)
Permission Errors: Ensure the DBSnapper user has:
SELECTpermissions on source databaseCREATE DATABASEpermissions on destination server
Get Help¶
- Configuration Reference - Complete configuration options
- Command Reference - Full CLI documentation
- GitHub Issues - Report bugs or request features
- Community Support - Get help from the community