Targets
Targets are the foundation of DBSnapper Cloud's database snapshot management. A target defines the complete configuration for creating, sanitizing, storing, and sharing snapshots for a specific database workload.
Overview¶
Each target encapsulates:
- Source database connection - Where to snapshot data from
- Destination database connection - Where to load snapshots (optional)
- Storage configurations - Cloud storage for both raw and sanitized snapshots
- Sanitization rules - Data privacy and security transformations
- Team sharing settings - Access control for collaborative workflows
Targets enable teams to standardize database snapshot processes while maintaining security and compliance requirements.
Managing Targets¶
Viewing All Targets¶
The Targets page displays all your configured targets along with any shared team targets you have access to. Shared team targets are available when your organization uses SSO integration, leveraging SSO groups to manage access permissions.

Each target shows:
- Target name and database type
- Connection status and last snapshot date
- Storage configuration and sharing permissions
- Quick actions for building snapshots or viewing details
Creating and Editing Targets¶
Click the Add Target button to create a new target or select an existing target to modify its configuration.
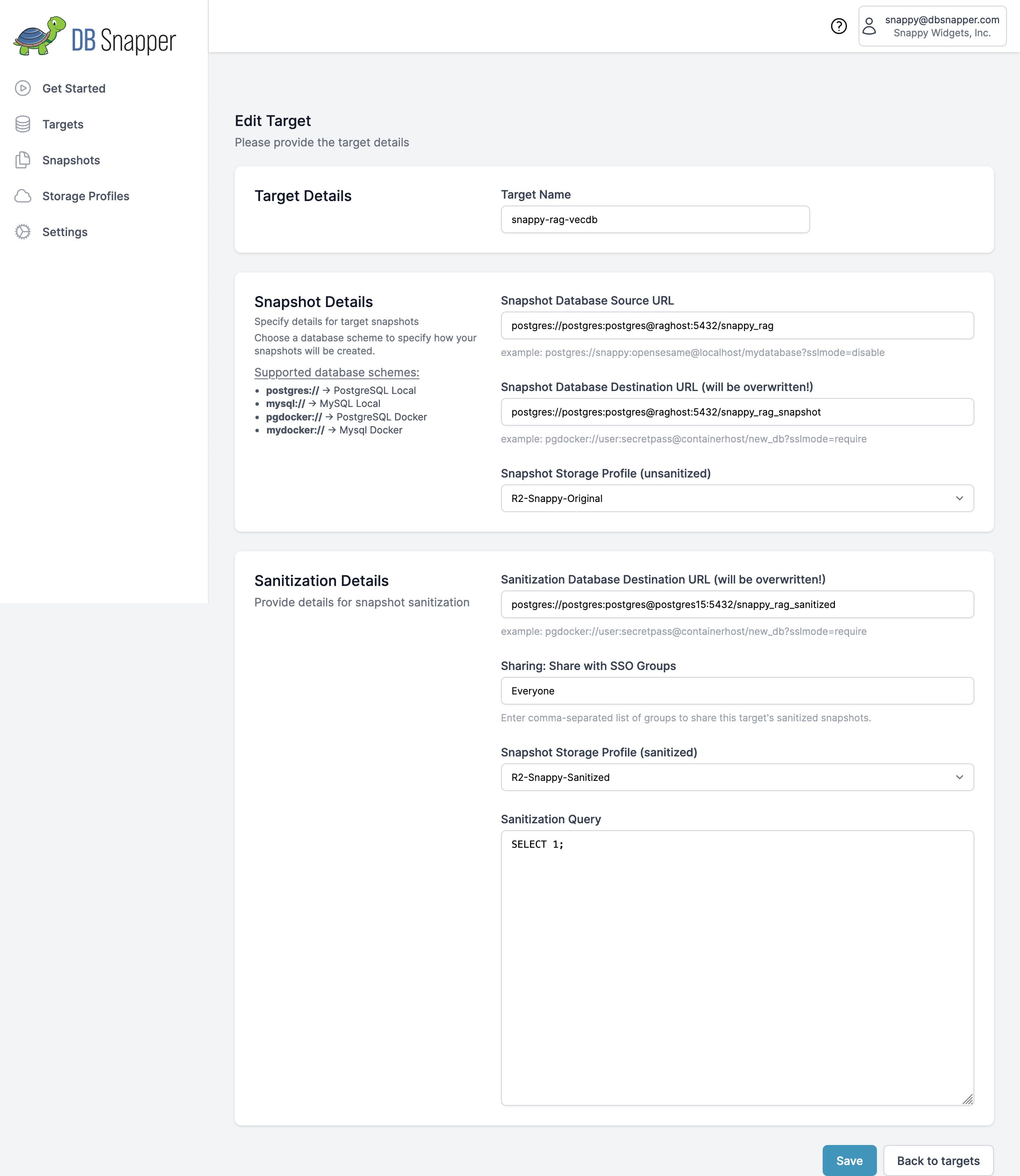
Target Configuration¶
When creating or editing a target, you'll configure several key components that define how snapshots are created, processed, and shared.
Basic Information¶
- Target Name
- A unique, descriptive name for this target (e.g., "production-users-db", "staging-analytics")
Database Connections¶
- Source Database URL (Required)
- The connection string for the database you want to snapshot
postgresql://username:password@host:port/database?sslmode=require
mysql://username:password@host:port/database
- Destination Database URL (Optional)
- Where snapshots will be loaded for development/testing
Destructive Operation
The destination database will be completely dropped and recreated when loading snapshots. Never use production databases as destinations.
Storage Configuration¶
- Unsanitized Storage Profile (Required)
- Storage profile where raw database snapshots are stored. These contain original production data and should have restricted access.
- Sanitized Storage Profile (Optional)
- Storage profile where sanitized snapshots are stored. These can be shared more broadly since sensitive data has been removed.
Security Best Practice
Use separate storage profiles for unsanitized and sanitized snapshots to implement proper access controls.
Data Sanitization¶
- Sanitization Database URL (Optional)
- Temporary database used for sanitization processing. If not specified, DBSnapper uses ephemeral Docker containers.
- Sanitization Query (Optional)
- SQL commands to remove or mask sensitive data during the sanitization process
-- Example sanitization query
UPDATE users SET
email = CONCAT('user', id, '@example.com'),
phone = '555-0000',
ssn = NULL;
DELETE FROM audit_logs WHERE created_at < NOW() - INTERVAL 30 DAY;
Team Collaboration¶
- SSO Group Sharing (Optional)
- Comma-separated list of SSO groups that can access sanitized snapshots from this target
SSO Required
Team sharing requires your organization to have SSO integration configured.
Working with Targets¶
Using the DBSnapper Agent¶
Once targets are configured in DBSnapper Cloud, you can use them with the DBSnapper Agent CLI:
# Build a snapshot using a cloud-configured target
dbsnapper build my-production-target
# Load a sanitized snapshot
dbsnapper load my-production-target latest
# Pull snapshots from cloud storage
dbsnapper pull my-production-target
Team Workflow Example¶
- DevOps Engineer creates target with production database connection and sanitization rules
- Development Team uses the target to create sanitized snapshots for local development
- QA Team accesses shared sanitized snapshots for consistent testing environments
- Data Team uses sanitized snapshots for analytics without exposing sensitive data
Security Considerations¶
- Connection Strings: Use environment variable templating to avoid storing credentials in target configurations
- Access Control: Leverage SSO groups to manage team access to sensitive targets
- Storage Separation: Use different storage profiles for unsanitized vs sanitized snapshots
- Audit Trail: Monitor target usage through DBSnapper Cloud's audit logging
Best Practices¶
Target Naming¶
Use descriptive, consistent naming conventions:
- Include environment:
prod-users-db,staging-analytics - Include purpose:
users-db-for-testing,analytics-weekly-snapshot - Avoid spaces and special characters
Connection Security¶
- Use read-only users for source database connections when possible
- Enable SSL/TLS for all database connections
- Use connection pooling for high-frequency snapshot operations
- Test connectivity before saving target configurations
Sanitization Strategy¶
- Start simple with basic field masking, then iterate
- Preserve referential integrity when sanitizing related data
- Test sanitization queries thoroughly before production use
- Document sanitization rules for compliance audits
Next Steps¶
- Configure Storage Profiles - Set up cloud storage for your snapshots
- Set up SSO Integration - Enable team collaboration features
- Sanitization Guide - Learn advanced data sanitization techniques
- Agent CLI Reference - Complete command-line interface documentation