Database Targets: Your Team's Snapshot Workflows¶
Database targets are where DBSnapper Cloud transforms individual database snapshots into team-wide collaborative workflows. A target defines everything needed to safely snapshot production data, sanitize it for security compliance, and share it with the right team members—all while maintaining your organization's data sovereignty.
Why Team-Managed Database Targets?¶
🎯 From Individual Chaos to Team Coordination¶
Before DBSnapper Cloud Targets: - Each developer creates their own snapshots with different sanitization approaches - QA teams can't reproduce bugs due to inconsistent test data - Production database access becomes a security and compliance nightmare - New team members spend days figuring out how to get realistic development data
With Centralized Target Management: - DevOps engineers define production targets once with proper sanitization rules - All team members automatically get access to consistent, sanitized snapshots - Security teams have centralized control over data access and audit trails - Compliance requirements are built into the snapshot creation process
🚀 V3.0 Performance at Enterprise Scale¶
DBSnapper Cloud targets leverage v3.0's multi-core architecture to deliver enterprise-grade performance:
targets:
large_production_db:
cpus: 8 # Use 8 cores for this high-volume database
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://prod-cluster:5432/large_app"
schema_config:
include_schemas: ["public", "analytics"] # Only snapshot relevant schemas
storage_profile: prod_s3
sanitize:
storage_profile: team_s3 # Sanitized snapshots shared with team
override_query: |
UPDATE users SET
email = CONCAT('user', id, '@example.com'),
ssn = NULL,
phone = '555-0000';
sso_groups: ["developers", "qa-team"]
What This Achieves: - Faster snapshots using multi-core PostgreSQL operations - Targeted data capture with schema filtering (PostgreSQL) - Automatic sanitization with centralized compliance rules - Secure sharing through SSO group-based access control
Team Target Management¶
🎛️ Centralized Target Dashboard¶
The DBSnapper Cloud targets dashboard gives you complete visibility into your organization's database snapshot ecosystem:
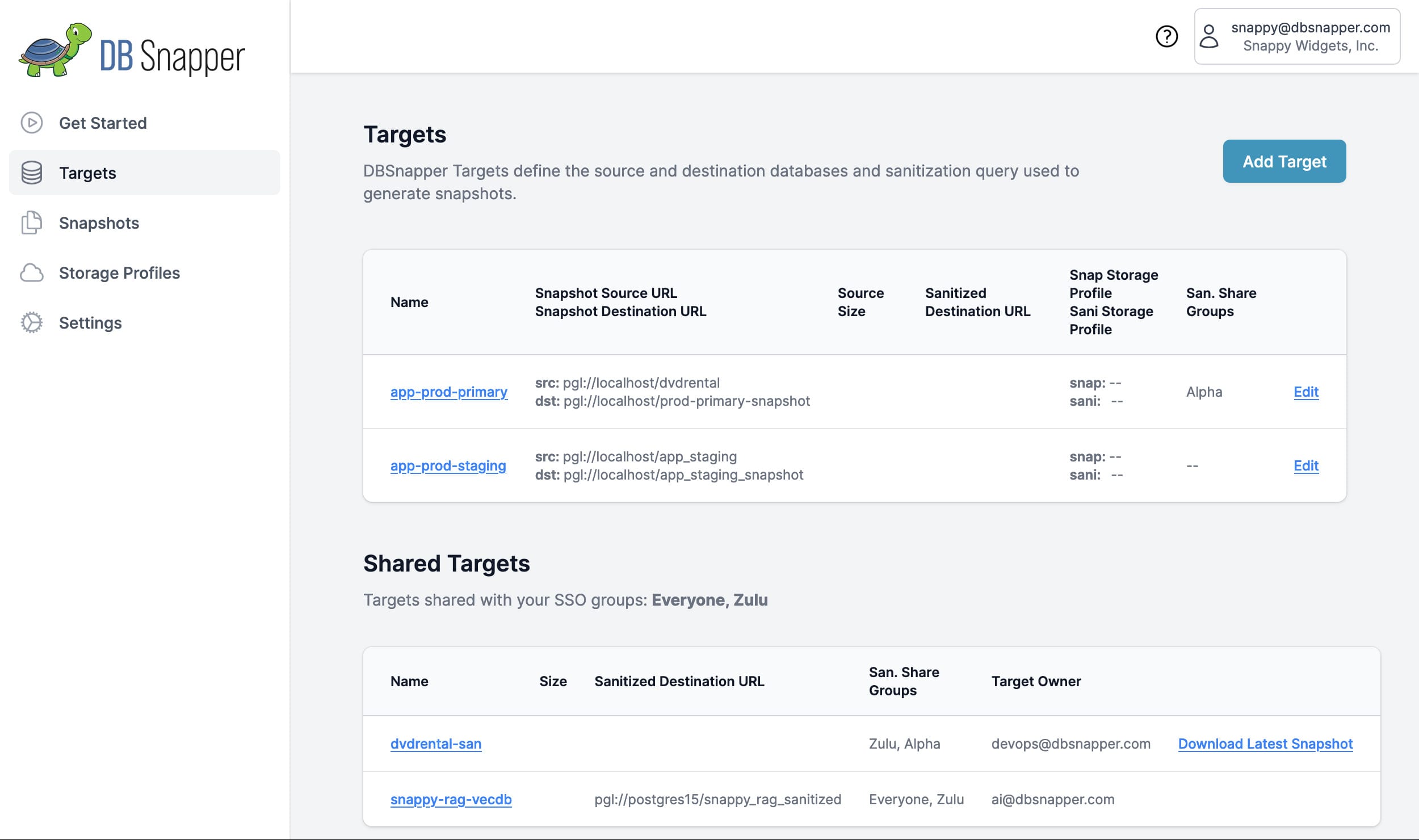
What You See:
- Your Targets - Database targets you've created and manage
- Shared Team Targets - Targets shared via SSO groups that you have access to
- Connection Status - Real-time connectivity and health monitoring
- Recent Activity - Latest snapshots, sanitization runs, and team access
- Performance Metrics - Snapshot creation times and storage usage
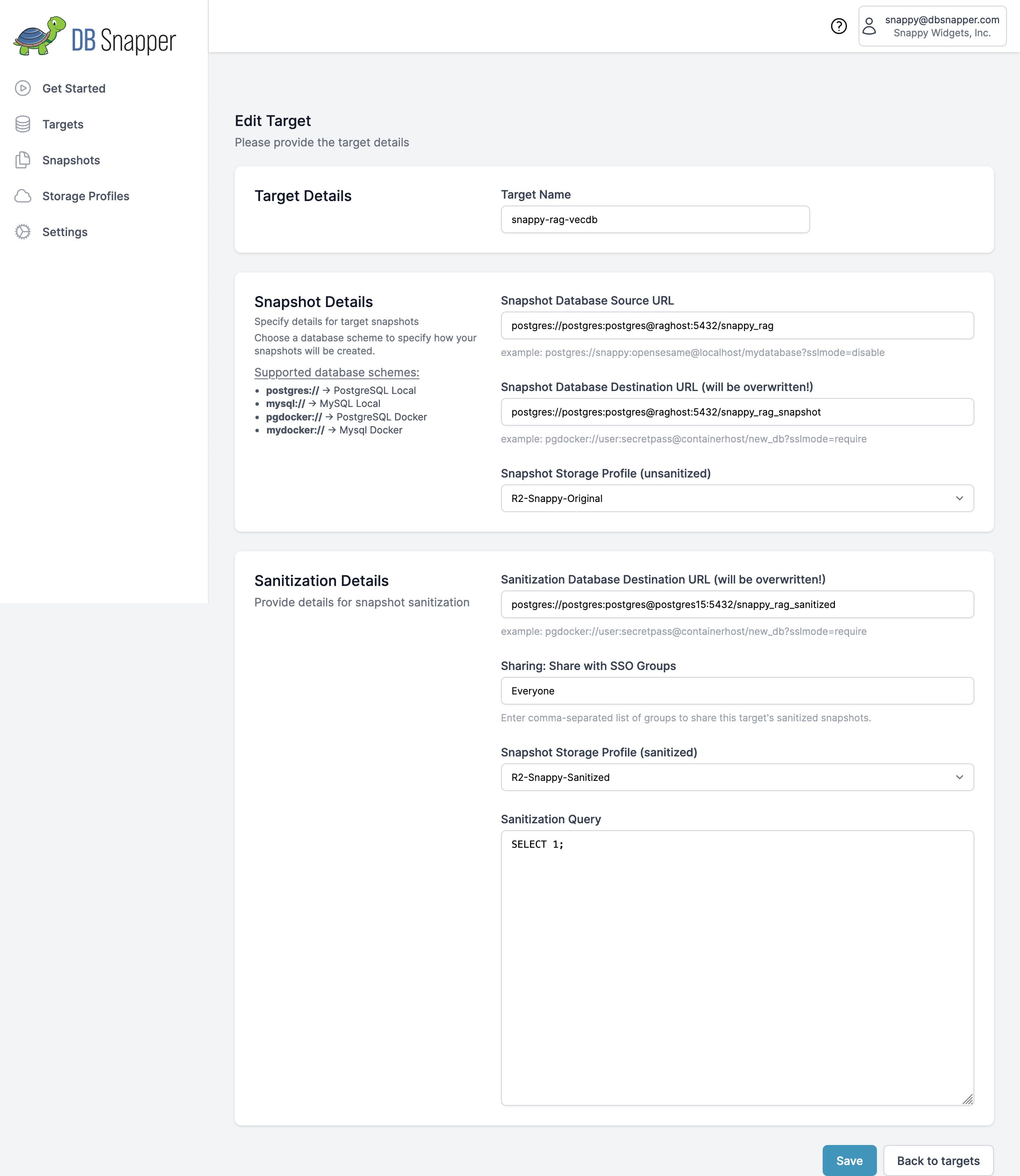
⚙️ Target Configuration Workflow¶
Visual target configuration for most users:
- Navigate to Targets in DBSnapper Cloud
- Click "Add Target" to create new or edit existing
- Configure all settings using the intuitive form interface
- Test connectivity before saving
- Team members immediately gain access based on SSO group membership
Advanced users can define targets locally that sync to the cloud:
# Define targets locally - automatically synced when authtoken present
authtoken: your-dbsnapper-cloud-token
targets:
production_api:
cpus: 6 # v3.0 multi-core configuration
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://{{`DB_USER` | env}}:{{`DB_PASS` | env}}@prod:5432/api"
dst_url: "postgresql://{{`DB_USER` | env}}:{{`DB_PASS` | env}}@dev:5432/api_dev"
schema_config:
include_schemas: ["public", "api_data"]
storage_profile: prod_s3
sanitize:
storage_profile: sanitized_s3
override_query: |
-- Comprehensive sanitization for GDPR compliance
UPDATE users SET
email = CONCAT('user', id, '@example.com'),
first_name = 'User',
last_name = CAST(id AS VARCHAR(10)),
phone = '555-0000',
ssn = NULL;
DELETE FROM audit_logs WHERE created_at < NOW() - INTERVAL '90 days';
sso_groups: ["developers", "qa-team"]
Terraform provider for enterprise infrastructure management:
resource "dbsnapper_target" "production_api" {
name = "production-api"
snapshot_config {
src_url = "postgresql://${var.db_user}:${var.db_password}@prod:5432/api"
dst_url = "postgresql://${var.db_user}:${var.db_password}@dev:5432/api_dev"
cpus = 6
schema_config {
include_schemas = ["public", "api_data"]
}
}
storage_profile = dbsnapper_storage_profile.prod_s3.name
sanitization {
storage_profile = dbsnapper_storage_profile.sanitized_s3.name
override_query = file("${path.module}/sanitization/api_sanitize.sql")
}
sso_groups = ["developers", "qa-team"]
}
Complete Target Configuration Guide¶
📋 Core Target Settings¶
- Target Name
- Unique identifier used across all DBSnapper tools and integrations
- CPU Configuration (New in v3.0)
- Optimize snapshot performance for your infrastructure
- Source Database URL (Required)
- Production database to snapshot from
- Destination Database URL (Optional)
- Development/testing database where snapshots are loaded
Destructive Operation
Loading snapshots completely replaces the destination database. Never use production databases as destinations.
Advanced PostgreSQL schema filtering for targeted snapshots:
targets:
large_production_app:
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://user:pass@prod:5432/large_app"
schema_config:
# Option 1: Include only specific schemas
include_schemas: ["public", "analytics", "reporting"]
# Option 2: Exclude specific schemas (alternative to include_schemas)
# exclude_schemas: ["temp_data", "logs", "debug"]
# Option 3: Include all schemas (override default behavior)
# use_default_schema: false
Schema Configuration Benefits: - Faster snapshots by excluding unnecessary schemas - Smaller storage usage with targeted data capture - Cleaner development environments without production logs/temp data - Compliance-focused by excluding sensitive operational schemas
☁️ Storage & Security Configuration¶
Implement proper data access boundaries:
targets:
production_users:
# Raw production data - restricted access
storage_profile: production_restricted_s3
sanitize:
# Sanitized data - broader team access
storage_profile: team_shared_s3
override_query: |
-- Remove PII while maintaining data utility
UPDATE users SET
email = CONCAT('user', id, '@example.com'),
phone = REGEXP_REPLACE(phone, '\\d', '5', 'g'),
ssn = NULL,
address = 'Test Address';
Three-tier sanitization system for maximum flexibility:
Priority 1: Target-Level Override (Highest Priority)
targets:
users_api:
sanitize:
override_query: |
-- Target-specific sanitization rules
UPDATE users SET email = CONCAT('user', id, '@example.com');
UPDATE orders SET customer_notes = 'Test order notes';
Priority 2: Global Override (Medium Priority)
# Applied to all targets unless overridden
override:
san_query: |
-- Organization-wide sanitization standards
UPDATE users SET ssn = NULL, phone = '555-0000';
Priority 3: Query File (Lowest Priority)
SSO group-based sharing for secure collaboration:
targets:
# Basic sharing
users_database:
sso_groups: ["developers", "qa-team"]
# Restricted sharing for sensitive data
financial_reports:
sso_groups: ["senior-developers", "finance-team", "compliance-auditors"]
# Public sharing for reference data
product_catalog:
sso_groups: ["all-engineering", "marketing", "customer-support"]
Access Control Benefits:
- Automatic provisioning - New team members get access based on SSO groups
- Centralized management - IT manages access through your existing identity provider
- Audit compliance - Complete trail of who accessed what data when
- Granular permissions - Different data sensitivity levels for different teams
⚡ V3.0 Performance & Container Optimization¶
Optimize snapshot operations for your infrastructure:
# Global performance defaults
defaults:
cpus: 4 # All targets use 4 cores unless overridden
targets:
# Small database - use fewer resources
reference_data:
cpus: 1
# Large production database - maximize performance
user_analytics:
cpus: 12 # Use all available cores for large datasets
snapshot:
schema_config:
exclude_schemas: ["logs", "temp_data"] # Reduce data volume
Perfect for Kubernetes and Docker environments:
# Container resource alignment
targets:
containerized_app:
cpus: 4 # Matches Kubernetes resource limits
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://{{`DB_HOST` | env}}:5432/{{`DB_NAME` | env}}"
storage_profile: container_s3
# Container-optimized sanitization
sanitize:
# Uses ephemeral Docker containers (no permanent database needed)
override_query: |
UPDATE users SET email = 'user@example.com';
Real-World Team Workflows¶
🔄 Complete Development Lifecycle¶
graph TB
A[DevOps Engineer] -->|Creates Target| B[DBSnapper Cloud]
B -->|Configures| C[Production DB]
B -->|Sanitizes & Stores| D[Team Storage]
D --> E[Developer Laptop]
D --> F[QA Environment]
D --> G[CI/CD Pipeline]
D --> H[Staging Environment]
E -->|dbsnapper load api-prod| E1[Local Dev DB]
F -->|Automated Load| F1[QA Testing DB]
G -->|Integration Tests| G1[Test DB]
H -->|Pre-Production| H1[Staging DB]👨💼 Role-Based Workflows¶
# 1. Create target with comprehensive configuration
targets:
production_users_api:
cpus: 8
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://readonly_user:{{`RO_PASS` | env}}@prod-cluster:5432/users_api"
schema_config:
exclude_schemas: ["audit_logs", "temp_data"]
storage_profile: prod_secure_s3
sanitize:
storage_profile: team_shared_s3
override_query: |
-- GDPR-compliant sanitization
UPDATE users SET
email = CONCAT('user', id, '@example.com'),
first_name = 'Test',
last_name = 'User' || id,
phone = '555-0000',
ssn = NULL,
date_of_birth = '1990-01-01';
DELETE FROM user_sessions;
DELETE FROM audit_logs WHERE created_at < NOW() - INTERVAL '30 days';
sso_groups: ["backend-developers", "qa-engineers", "data-analysts"]
# Check available targets (shows both local and cloud targets)
dbsnapper targets
# Load latest sanitized snapshot for development
dbsnapper load production_users_api
# Or load specific snapshot
dbsnapper load production_users_api 2 # Load 2nd most recent
# Check target details and available snapshots
dbsnapper target production_users_api
# GitHub Actions workflow
name: Integration Tests
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: dbsnapper/install-dbsnapper-agent-action@v1
- name: Load test database
run: |
# Cloud target automatically provides latest sanitized snapshot
dbsnapper load production_users_api
- name: Run integration tests
run: |
# Tests run against realistic production-like data
npm run test:integration
🔒 Enterprise Security & Compliance¶
targets:
# Production - highly restricted
prod_users_api:
sso_groups: ["devops-team", "senior-engineers"]
sanitize:
storage_profile: compliance_s3
# Staging - broader access
staging_users_api:
sso_groups: ["backend-developers", "qa-engineers", "product-managers"]
# Reference data - open access
product_catalog:
sso_groups: ["all-engineering", "marketing", "customer-support"]
# All target access is logged in DBSnapper Cloud
# Compliance team can review:
# - Who accessed which targets when
# - What sanitization rules were applied
# - Where snapshots were stored and retrieved
# - Performance and usage metrics
# Example audit query capabilities:
# "Show all access to production_users_api target in the last 30 days"
# "List all users who downloaded sanitized financial_reports snapshots"
# "Verify PII sanitization was applied to all shared snapshots"
Production Best Practices¶
🏗️ Target Architecture Patterns¶
# Separate targets for different environments
targets:
prod_api_database:
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://readonly@prod-cluster:5432/api"
sso_groups: ["devops", "senior-developers"]
staging_api_database:
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://user@staging-db:5432/api"
sso_groups: ["developers", "qa-team"]
dev_api_database:
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://user@dev-db:5432/api"
sso_groups: ["all-developers"]
# Separate targets for different microservices
targets:
users_service_prod:
cpus: 6
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://readonly@users-db:5432/users"
schema_config:
include_schemas: ["public", "user_data"]
orders_service_prod:
cpus: 4
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://readonly@orders-db:5432/orders"
schema_config:
include_schemas: ["public", "order_data"]
analytics_service_prod:
cpus: 12 # Large analytics database
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://readonly@analytics-cluster:5432/analytics"
schema_config:
exclude_schemas: ["temp_calculations", "debug_logs"]
🔐 Security Implementation¶
Connection Security:
# Use dedicated read-only users for snapshots
targets:
secure_production:
snapshot:
# Read-only user with minimal permissions
src_url: "postgresql://dbsnapper_readonly:{{`READONLY_PASS` | env}}@prod:5432/app?sslmode=require"
# Development database (can be overwritten)
dst_url: "postgresql://dev_user:{{`DEV_PASS` | env}}@dev:5432/app_dev?sslmode=require"
Network Security: - Use SSL/TLS for all database connections - Implement database firewall rules for DBSnapper agent IPs - Use VPC peering or private networks when possible - Enable connection pooling for high-frequency operations
Credential Management: - Store sensitive credentials as environment variables - Use AWS IAM roles or equivalent cloud identity systems - Implement regular credential rotation - Avoid hardcoding credentials in configuration files
📊 Performance Optimization¶
# Optimize for your infrastructure and data size
targets:
large_analytical_db:
cpus: 16 # Use all available cores
snapshot:
src_url: "postgresql://user@analytics-cluster:5432/warehouse"
schema_config:
# Only capture relevant schemas to reduce size/time
include_schemas: ["marts", "dimensions", "facts"]
exclude_schemas: ["staging", "temp", "logs"]
# Use high-performance storage for large databases
storage_profile: nvme_optimized_s3
sanitize:
# Sanitized version can use standard storage
storage_profile: standard_team_s3
override_query: |
-- Minimal sanitization to preserve analytical utility
UPDATE customers SET
name = 'Customer ' || id,
email = CONCAT('customer', id, '@example.com');
Performance Best Practices:
- Use CPU configuration to match your infrastructure capabilities
- Implement schema filtering to reduce snapshot size and time
- Choose storage regions close to your database infrastructure
- Monitor snapshot creation times and optimize accordingly
- Use separate storage profiles for different performance requirements
Troubleshooting & Validation¶
🔧 Target Testing & Validation¶
# Test target connectivity and configuration
dbsnapper config check --target production_api
# Validate storage profile connectivity
dbsnapper config check --storage-profile team_s3
# Dry run to verify configuration without creating snapshot
dbsnapper build production_api --dry-run
# Test complete workflow
dbsnapper build test_target && dbsnapper load test_target
🚨 Common Issues & Solutions¶
Solutions:
- Verify database credentials and connection string format
- Check network connectivity and firewall rules
- Ensure database user has required permissions (SELECT for source, CREATE/DROP for destination)
- Test connection manually: psql "postgresql://user:pass@host:5432/db"
Solutions: - Grant appropriate database permissions to DBSnapper user - Use dedicated read-only user for source database connections - Verify SSL/TLS configuration if required - Check that destination database user has CREATE/DROP privileges
Next Steps & Integration¶
🎯 Recommended Next Actions¶
- Complete Storage Setup - Configure secure cloud storage for your snapshots
- Enable SSO Integration - Set up team authentication and access control
- Explore Advanced Sanitization - Learn comprehensive data privacy techniques
- Set up CI/CD Integration - Automate snapshots in your development pipeline
🔗 Modern Development Integration¶
Available Integrations: - VS Code Extension - Manage targets directly from your editor - GitHub Actions - Automated snapshots in CI/CD pipelines - Terraform Provider - Infrastructure as Code management - MCP Server - AI assistant integration for database operations
Ready to create your first team target? Start by configuring storage profiles for secure cloud snapshot storage, then return here to create targets that your entire team can access.
Need complete implementation guidance? Check out our Team Workflows guide for end-to-end workflows covering DevOps setup, daily developer usage, QA testing, and compliance processes.