Storage Profiles: Secure Cloud Storage for Database Snapshots¶
Storage Profiles define where and how your database snapshots are stored in cloud storage providers. They're essential for team collaboration, backup strategies, and implementing proper security boundaries between raw and sanitized data.
Why Cloud Storage for Database Snapshots?¶
🔗 Team Collaboration¶
Enable seamless snapshot sharing across your organization:
- Developers can access the latest sanitized snapshots instantly
- QA teams get consistent test data for reliable bug reproduction
- CI/CD pipelines automatically use up-to-date snapshots
🛡️ Security Boundaries¶
Implement proper data access controls: - Raw snapshots → Restricted storage (production team access only) - Sanitized snapshots → Shared storage (broader team access) - Audit trails → Track all snapshot access and modifications
💰 Cost Efficiency¶
Optimize storage costs and performance: - Compressed snapshots typically use 10-50% of original database size - Lifecycle policies automatically manage snapshot retention - Multi-region storage for disaster recovery scenarios
Supported Cloud Storage Providers¶
DBSnapper follows a "Bring Your Own Cloud Storage" approach—use your existing cloud storage accounts with your security policies and access controls.
Full S3 ecosystem support:
storage_profiles:
production_s3:
provider: s3
region: us-west-2
bucket: dbsnapper-prod-snapshots
prefix: raw-snapshots
awscli_profile: production # Use AWS CLI credentials
sanitized_s3:
provider: s3
region: us-west-2
bucket: dbsnapper-team-snapshots
prefix: sanitized-snapshots
awscli_profile: team-access # Different credentials for team access
Benefits: - Integrated with your existing AWS IAM policies - Server-side encryption (SSE-S3, SSE-KMS) - Intelligent tiering for cost optimization - Cross-region replication for disaster recovery
Zero egress fees with global performance:
storage_profiles:
r2_sanitized:
provider: r2
bucket: dbsnapper-r2-sanitized
prefix: team-snapshots
account_id: your-cloudflare-account-id
awscli_profile: r2_profile # Configure AWS CLI for R2
Benefits: - Zero egress charges (significant cost savings) - Global edge network for fast access - S3-compatible API (works with existing tools) - Built-in DDoS protection
Complete control with on-premises or private cloud:
storage_profiles:
minio_local:
provider: minio
endpoint: https://minio.yourcompany.com
bucket: dbsnapper-snapshots
prefix: production
access_key: your-minio-access-key
secret_key: your-minio-secret-key
Benefits: - Complete data sovereignty - No vendor lock-in - Kubernetes-native deployments - Full control over security and compliance
Creating Storage Profiles¶
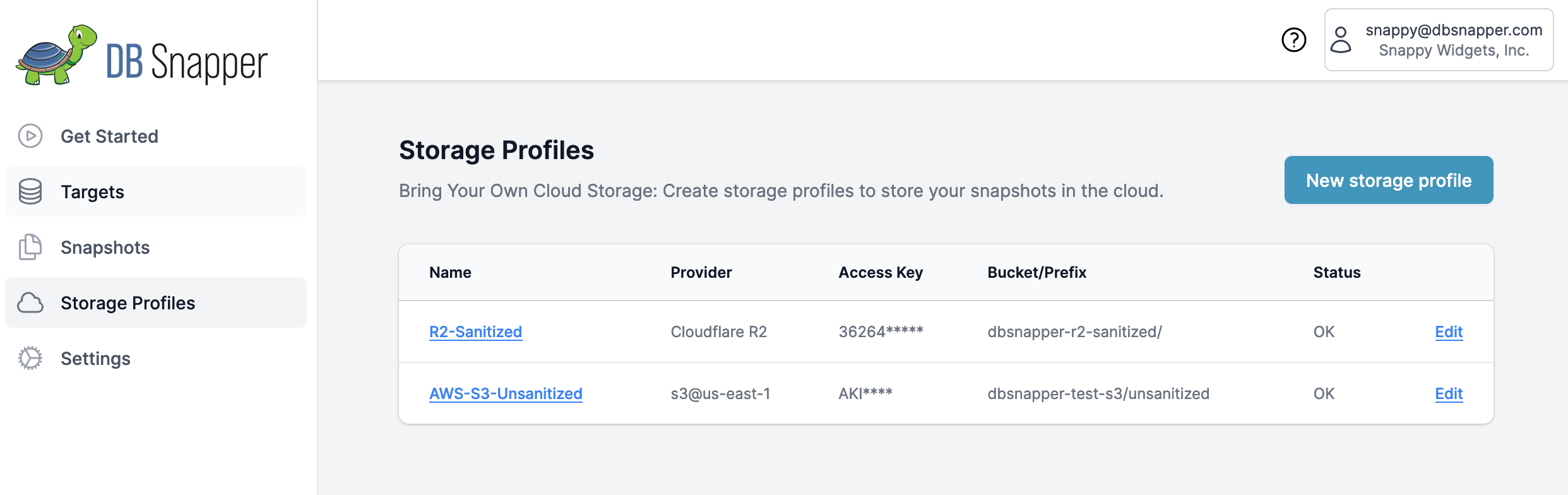
Option 1: DBSnapper Cloud Web Interface¶
Visual Configuration (Recommended for most users):
- Navigate to Storage Profiles in DBSnapper Cloud
- Click "New Storage Profile" to create a profile
- Configure Provider Settings using the forms below
- Test connectivity before saving
Option 2: Local Configuration File¶
Advanced users can define storage profiles in their local configuration:
# Define storage profiles locally (synced to cloud when authtoken present)
storage_profiles:
prod_s3:
provider: s3
region: us-west-2
bucket: mycompany-db-snapshots
prefix: production
awscli_profile: dbsnapper-prod
team_r2:
provider: r2
bucket: team-sanitized-data
prefix: shared
account_id: your-account-id
awscli_profile: r2_team
# Use in targets
targets:
production_api:
storage_profile: prod_s3 # Raw snapshots go here
sanitize:
storage_profile: team_r2 # Sanitized snapshots shared here
Storage Profile Configuration¶
Basic Configuration¶
- Profile Name
- Unique identifier for this storage profile (used in target configuration)
- Provider
- Cloud storage provider (s3, r2, minio, dospaces)
- Bucket
- Storage bucket/container name where snapshots will be stored
- Prefix (Optional)
- Folder/path prefix for organizing snapshots (e.g.,
production/,team-snapshots/)
Authentication Methods¶
Most secure approach using your existing AWS CLI configuration:
# Configure AWS CLI profile for DBSnapper
aws configure --profile dbsnapper-prod
# Configure additional profile for R2
aws configure --profile r2_team \
--endpoint-url https://your-account-id.r2.cloudflarestorage.com
storage_profiles:
secure_s3:
provider: s3
bucket: secure-snapshots
awscli_profile: dbsnapper-prod # Uses existing CLI credentials
Benefits: - Credentials stored in standard AWS CLI location - Supports MFA and role assumption - Works with AWS SSO and temporary credentials - No credentials in DBSnapper configuration files
For environments where AWS CLI profiles aren't available:
Security Best Practices¶
📊 Implement Storage Separation¶
Use different storage profiles for different security boundaries:
targets:
production_database:
# Raw production data - highly restricted access
storage_profile: raw_prod_s3
sanitize:
# Sanitized data - broader team access
storage_profile: sanitized_team_s3
override_query: "UPDATE users SET email = CONCAT('user', id, '@example.com')"
# Share only sanitized snapshots with these groups
sso_groups: ["developers", "qa-team"]
🔒 Encryption Configuration¶
Enable encryption at rest for sensitive snapshots:
🔍 Access Control & Monitoring¶
Implement comprehensive access controls:
# Production raw data - restricted access
storage_profiles:
production_raw:
provider: s3
bucket: dbsnapper-production-raw
awscli_profile: production_restricted
# Only DevOps team has access to this profile
# Team sanitized data - broader access
team_sanitized:
provider: s3
bucket: dbsnapper-team-sanitized
awscli_profile: team_shared
# All developers can access sanitized snapshots
Monitoring and Audit: - Enable S3/R2 access logging to track snapshot usage - Set up CloudTrail (AWS) or equivalent monitoring for API calls - Configure alerts for unusual access patterns - Regular review of storage costs and usage patterns
Performance Optimization¶
📈 Upload/Download Performance¶
Optimize for large database snapshots:
# Use regions close to your database infrastructure
storage_profiles:
optimized_s3:
provider: s3
region: us-west-2 # Same region as your RDS/Aurora instances
bucket: dbsnapper-optimized
prefix: snapshots
Performance Tips: - Region Selection: Choose storage regions close to your databases - Multipart Uploads: Automatically handled for large snapshots - Compression: DBSnapper automatically compresses snapshots (typically 10-50% size reduction) - Parallel Operations: V3.0 multi-core operations improve upload speeds
💰 Cost Optimization¶
Implement intelligent storage lifecycle policies:
Cloudflare R2 advantages: - Zero egress fees (major cost savings) - Competitive storage pricing - No charges for API requests - Global edge network for performance
Troubleshooting¶
🔧 Common Issues & Solutions¶
Connection Test Failures:
# Test storage profile connectivity
dbsnapper config check --storage-profile production_s3
# Test with debug information
DBSNAPPER_DEBUG=true dbsnapper config check --storage-profile production_s3
Common Problems:
Solutions:
1. Verify AWS CLI profile exists: aws configure list --profile dbsnapper-prod
2. Test profile access: aws s3 ls s3://your-bucket --profile dbsnapper-prod
3. Check IAM permissions include s3:ListBucket
4. Ensure profile name matches storage profile configuration
Solutions: 1. Verify bucket exists and is accessible 2. Check IAM policy includes required S3 permissions 3. Confirm bucket region matches profile configuration 4. Test with minimal IAM policy first, then expand
🔍 Validation and Testing¶
Validate storage profile configuration:
# Check all storage profiles
dbsnapper config validate --storage-profiles
# Test specific profile with verbose output
dbsnapper config check --storage-profile team_s3 --verbose
# Test upload/download cycle
dbsnapper build test-target --dry-run # Verify configuration without creating snapshot
Migration and Management¶
🚀 Migrating Between Storage Providers¶
Example: Migrating from S3 to R2:
# 1. Create new R2 storage profile
storage_profiles:
new_r2:
provider: r2
bucket: migrated-snapshots
account_id: your-r2-account
awscli_profile: r2_profile
# 2. Update target to use new profile
targets:
production_api:
storage_profile: new_r2 # Changed from old S3 profile
Migration Process:
1. Create new storage profile with target provider
2. Test connectivity and permissions
3. Update targets to use new storage profile
4. Create new snapshots with new provider
5. Optionally migrate existing snapshots using cloud provider tools
📋 Storage Profile Management¶
Best practices for ongoing management:
- Naming Convention: Use descriptive names (
prod-raw-s3,team-sanitized-r2) - Documentation: Document which profiles are used by which teams
- Regular Audits: Review storage costs and access patterns monthly
- Credential Rotation: Regular rotation of access keys and secrets
- Backup Strategy: Consider multiple storage providers for critical snapshots
Next Steps¶
Now that you've configured storage profiles:
- Create Database Targets - Define your databases and link them to storage profiles
- Set up Team Access - Configure SSO for secure team collaboration
- Test Your Setup - Create your first cloud-stored snapshot
- GitHub Actions Integration - Connect with CI/CD and development tools
Need help with storage configuration? Check our Configuration Settings guide for comprehensive examples, or explore Cloud Storage detailed documentation for advanced scenarios.
Ready to implement complete team workflows? Our Team Workflows guide shows how storage profiles integrate with targets, SSO, and daily development processes for enterprise-scale database snapshot collaboration.